Prof. Hu Junqing from College of Health Science and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen Technology University (SZTU), published a tutorial review titled “Biodistribution, degradability and clearance of 2D materials for their biomedical applications” in Chemical Society Reviews (IF: 60.615) on September 1, together with Prof. Zhang Han from Shenzhen University and Prof. Xianfeng Chen from the University of Edinburgh as co-corresponding authors. Doctoral student Fan Taojian, Assistant Professor Yan Li and Dr. He Shiliang from College of Health Science and Environmental Engineering are the co-first authors and SZTU is the first affiliation. The full text of the review can be found at: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/cs/d1cs01070k.
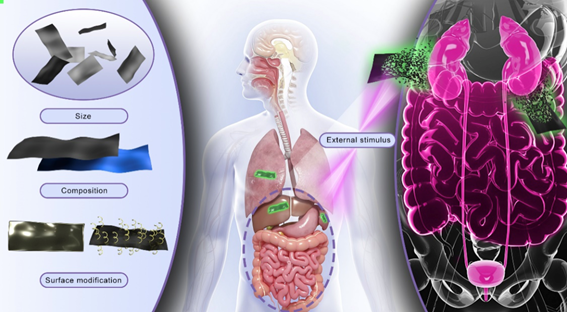
Schematic diagram of the in vivo fate of 2D materials [Photo/https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/cs/d1cs01070k]
With the rapid development of nanotechnology, increasing numbers of nanomaterials have shown unique advantages in the field of biomedicine and disease therapy. Among these candidate materials, 2D materials are attracting increasing attention as effective therapeutic and diagnostic agents. The review introduces 2D nanomaterials and their excellent properties, such as strong optical absorption and ultra-high photothermal conversion efficiency. It also comprehensively summarizes the strategies that are currently adopted for regulating the in vivo fate of 2D materials, including modulations of their size, surface properties, composition and external stimuli. The researchers introduce several classes of 2D materials with broad biomedical applications, such as graphene and its derivatives, monoelemental materials (Xenes), MXenes and transition metal dichalcogenides. They also propose the challenges and concerns of the future study of these 2D materials. To realize the clinical transformation, their biodistribution, degradation, and metabolism must be carefully investigated. The biological safety and metabolic pathways remain crucial concerns to be addressed.
The research group led by Professor Hu Junqing has achieved several results in the field of nanophotothermal reagents, such as high-efficiency and stable chalcogenide copper-based compound photothermal reagents, high-efficiency and degradable metal oxide photothermal reagents and ternary bimetallic sulfide nanophotothermal reagents and nanocomposite photothermal reagents with multi-modal imaging and combined therapy functions.
Tips: (Some information below is cited from the official website of Royal Society of Chemistry.)
Founded in 1972, Chemical Society Reviews is the Royal Society of Chemistry’s leading reviews journal. It publishes high-impact, authoritative and reader-friendly review articles covering important topics in chemistry, chemical engineering, materials, etc. The latest impact factor of the journal is 60.615.
Drafted by Daisy(姚琦)/ International Cooperation & Student Affairs Office
Revised by International Cooperation & Student Affairs Office
Edited by International Cooperation & Student Affairs Office
